In this article, you will learn the basics of calculating lot size in the Forex market. We will explain what a lot is and why it is important in trading. You will discover different methods to calculate lot size, including the formula to use for standard lots, mini lots, and micro-lots. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how to determine the appropriate lot size for your trades in Forex.
Introduction to Forex Trading
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is the buying and selling of currencies in the global marketplace. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily turnover of trillions of dollars. The Forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, allowing traders from around the world to participate at their convenience.
What is Forex?
Forex stands for foreign exchange, which refers to the conversion of one currency into another. Unlike other financial markets, Forex does not have a central exchange or physical location. Instead, it is a decentralized market where participants trade currencies electronically.
How does Forex trading work?
Forex trading involves speculating on the price movements of different currency pairs. When you trade Forex, you are essentially buying one currency and selling another at the same time. For example, if you believe that the euro will strengthen against the US dollar, you would buy the EUR/USD currency pair. If your prediction is correct and the euro does indeed increase in value relative to the US dollar, you would make a profit.
Importance of lot size in Forex trading
Lot size is a crucial aspect of Forex trading as it determines the position size for each trade. A position size refers to the number of lots or units of a currency pair you are trading. Properly calculating lot sizes is essential for managing risk, determining profit or loss, and ensuring effective money management in Forex trading.
Understanding Lot Size
Definition of lot size
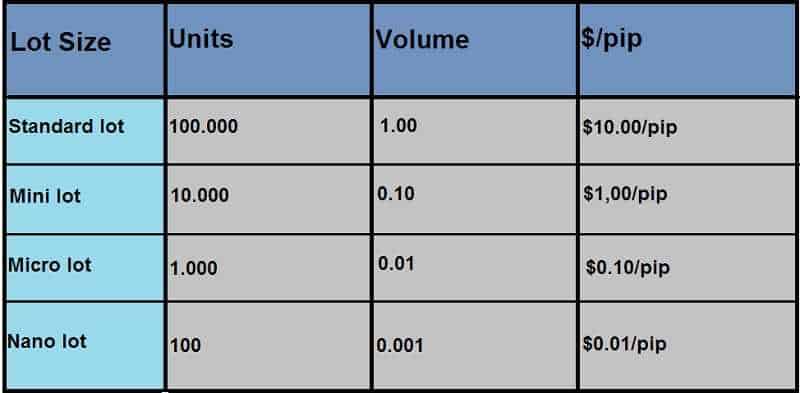
A lot refers to a standardized trading unit in Forex, representing a specific quantity of currency. Historically, a standard lot size was 100,000 units of the base currency. However, due to the growth and accessibility of the Forex market, smaller lot sizes are now available for traders with smaller capital.
Different types of lot size
In addition to the standard lot, there are also mini lots (10,000 units) and micro lots (1,000 units) available in Forex trading. These smaller lot sizes allow traders to engage in the market with lower capital requirements. Some brokers also offer nano lots, which are even smaller at 100 units.
Why lot size matters in Forex trading
Lot size plays a crucial role in managing risk and determining the potential profit or loss of a trade. Since Forex is a leveraged market, the size of your position influences the amount of money you can potentially make or lose. A larger lot size amplifies both profits and losses, while a smaller lot size limits the magnitude of gains and losses.
This image is property of a.c-dn.net.
Calculating Lot Size
Pip value calculation
To calculate the lot size, you first need to determine the pip value of the currency pair you are trading. A pip is the smallest incremental movement in the price of a currency pair. It represents one unit of the fourth decimal place in most currency pairs, except those involving the Japanese yen, where it represents the second decimal place.
To calculate the pip value, you need to know the exchange rate of the currency pair, the lot size, and the currency of your trading account. By multiplying the pip value by the number of pips gained or lost in a trade, you can determine the monetary value of the movement.
Determining risk percentage
Before calculating the lot size, it is essential to determine your risk percentage. Risk percentage refers to the maximum amount of capital you are willing to risk on a single trade. It is recommended to risk no more than 1-2% of your trading account on each trade to manage risk effectively.
Accounting for leverage and margin requirements
Leverage allows you to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital, but it also amplifies both profits and losses. Different brokers offer varying leverage options, so it is crucial to understand the leverage and margin requirements provided by your broker.
When calculating the lot size, you need to consider the amount of leverage you are using and the margin requirement set by your broker. The margin requirement is the amount of money you need to have in your trading account to open and maintain a position.
Factors to Consider
Risk tolerance
Your risk tolerance plays a significant role in determining the appropriate lot size for your trades. If you are risk-averse, you may opt for smaller lot sizes to limit potential losses. On the other hand, if you are comfortable with higher risk, you may choose larger lot sizes to maximize potential profits.
Capital availability
The amount of capital you have available for trading will influence your lot size. If you have a smaller trading account, it may be more appropriate to trade with mini or micro lots to avoid overexposure. Conversely, if you have a larger account, you may consider using standard lots to take advantage of potential profit opportunities.
Trading strategy and goals
Your trading strategy and goals should also guide your lot size determination. Different strategies may require specific lot sizes to align with their risk and reward objectives. For example, a scalping strategy may employ smaller lot sizes with tighter profit targets, while a long-term trend following strategy may use larger lot sizes with wider profit targets.
This image is property of traders-paradise.com.
Using Position Sizing Tools
Online calculators
Various online calculators are available to assist traders in calculating the appropriate lot size based on their risk and account specifications. These tools often take into account currency pair, account currency, leverage, and risk percentage to provide accurate lot size calculations.
Formula-based approach
Traders can also calculate lot sizes manually using a formula. The formula incorporates the account balance, risk percentage, stop-loss level, and pip value to determine the appropriate position size. While this approach requires more manual calculation, it allows for customization and flexibility.
Software applications
There are software applications and trading platforms that provide built-in position sizing tools and calculators. These applications automate the process of calculating lot sizes, taking into account various factors such as risk tolerance, account balance, and leverage. Using these tools can save time and ensure accurate position sizing.
Sample Scenarios
Calculating lot size for a specific trade
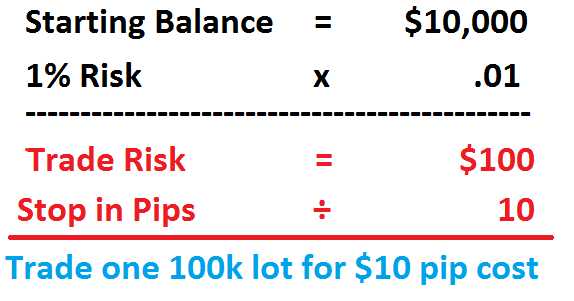
Suppose you have a trading account denominated in USD, and you want to trade the EUR/USD currency pair. Your account balance is $10,000, and you are willing to risk 1% of your capital on this trade. The exchange rate is 1.2000, and your stop-loss level is set at 50 pips.
To calculate the lot size, you need to determine the pip value first. In this case, the pip value is $10 (0.0001 divided by 1.2000, multiplied by $100,000 – the standard lot size). Given that your risk percentage is 1% and your account balance is $10,000, the maximum risk on this trade is $100 ($10,000 multiplied by 1%).
With a stop-loss of 50 pips, the maximum loss per pip is $0.50 ($100 divided by 50 pips). Therefore, the appropriate lot size for this trade would be 2 mini lots ($0.50 divided by $10).
Adjusting lot size for different currency pairs
Different currency pairs have varying pip values due to their exchange rate differences. For example, the pip value of the EUR/USD currency pair is different from that of the USD/JPY pair. Therefore, when trading different currency pairs, you must recalculate the lot size to align with your risk management strategy.
Scaling in and out of trades
In certain trading strategies, traders may choose to scale into a position by gradually increasing their lot size as the trade moves in their favor. Conversely, they may also scale out of a position by reducing their lot size as the trade approaches their target profit level. Scaling in and out of trades allows traders to adapt their lot size to market conditions and optimize their risk and reward potential.
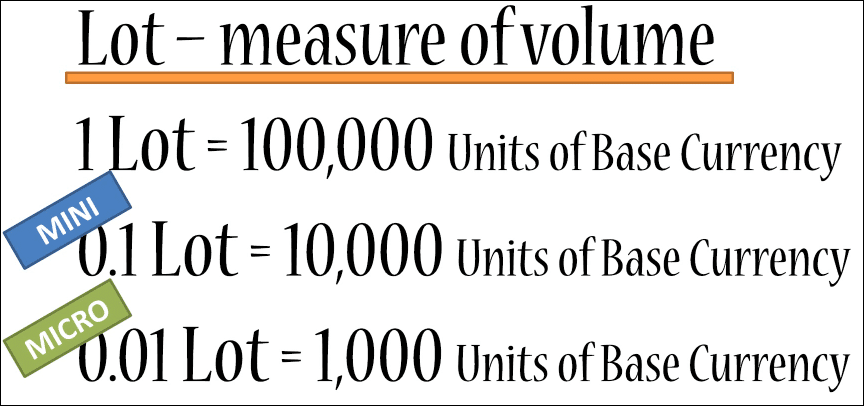
This image is property of www.forexboat.com.
Risk Management Techniques
Setting stop-loss and take-profit levels
Setting appropriate stop-loss and take-profit levels is crucial for managing risk in Forex trading. A stop-loss order is placed below the entry price to limit potential losses, while a take-profit order is placed above the entry price to secure potential profits. By setting these levels, traders can define their risk-reward ratio and ensure they are not exposed to excessive losses.
Using trailing stops
Trailing stops are stop-loss orders that automatically adjust as the trade moves in the trader’s favor. They allow traders to lock in profits while giving the trade room to breathe and potentially capture larger gains. Trailing stops can be a valuable tool in managing risk and maximizing profit potential.
Applying proper risk-reward ratios
An essential risk management technique is to ensure that the potential reward of a trade outweighs the potential risk. By maintaining a favorable risk-reward ratio, such as 1:2 or 1:3, traders can minimize losses and increase the profitability of their trades.
Psychology of Lot Sizing
Emotional factors in lot size determination
Lot size determination is not solely based on mathematical calculations but is also influenced by psychological factors. Traders’ emotions, such as fear and greed, can impact their lot size decisions. It is essential to remain rational and objective when determining lot sizes to avoid overexposure and emotional trading.
Overtrading and greed
Overtrading, or excessive trading, can occur when traders increase lot sizes beyond their risk management strategy. This behavior often stems from greed and the desire to make quick profits. Overtrading can lead to increased risks and potential losses, as traders deviate from their predefined risk parameters.
Staying disciplined in position sizing
Maintaining discipline in position sizing is crucial for consistent and successful Forex trading. Traders must adhere to their risk management strategy and resist the temptation to deviate from their predetermined lot sizes. Consistency and discipline in position sizing contribute to long-term profitability and risk control.
This image is property of cdn.litemarkets.com.
Monitoring and Adjusting Lot Sizes
Keeping track of trade performance
It is essential to monitor the performance of your trades and assess the effectiveness of your lot sizing strategy. By keeping track of your trade results, including profit and loss, you can identify patterns and make informed decisions regarding your position sizing strategy.
Evaluating and optimizing lot size
Regular evaluation of your lot size strategy is necessary to ensure its effectiveness. As market conditions change, it may be necessary to adjust your risk parameters and lot sizes accordingly. By analyzing past trades and market trends, you can optimize your lot size strategy for improved risk management and profitability.
Adapting to changing market conditions
The Forex market is dynamic and continually evolving. Traders must be adaptable to changing market conditions and adjust their lot sizes accordingly. A strategy that works in one market environment may not be suitable for another. Staying informed and flexible allows traders to adapt their lot size strategy to optimize performance.
Conclusion
Calculating lot size in Forex is a fundamental aspect of risk management and money management. By accurately determining the appropriate position size, traders can effectively manage risk, minimize losses, and maximize profitability. Factors such as risk tolerance, capital availability, and trading goals play a significant role in lot size determination. Using position sizing tools and techniques, as well as staying disciplined and adaptive, are essential for successful lot size strategies in Forex trading. Continuous learning and improvement in position sizing contribute to long-term success in the dynamic and ever-changing Forex market.